‘There’s no ecosystem without the recipients’
In an increasingly complex messaging ecosystem of CPaaS, aggregators, MNOs, campaign registration, and message filtering, we should remember that the ultimate power to read or ignore a message lies with the recipient. Stuart McBride, Director of Product Management at Enea, explored what message filtering tools are available to recipients and the implications for business messaging, at MEF Connects in Dublin.
Read on to learn about the message filtering tools available today, who uses them, and why it matters to the messaging ecosystem.
The Smartphone Experience: Apple vs Android
With a 98% open rate, SMS is an excellent channel to reach people. However, the way we receive SMS has changed. In the era of the Smartphone, vendors like Apple and Android want their users to have a “Smartphone experience.” So, how is this technology applied to SMS recipients’ inboxes, and what impact is it having on how they interact with messages? First, let’s cover the technology.
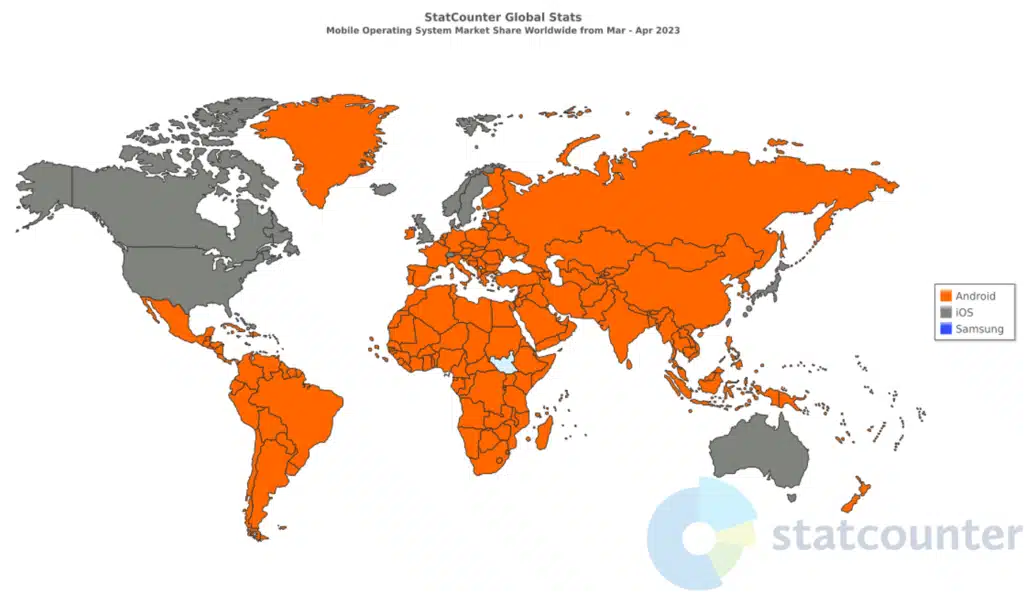
Apple and Android have slightly different approaches to their relationships with users. Apple views the user experience as key, with tightly controlled interfaces, avoiding third party services and partners where possible. Android takes a more flexible approach, and is open to input from third party software and Apps. The map below shows the distribution of IOS users compared to Android users, where grey represents an IOS majority, and orange represents an Android majority.
Distribution of IOS vs Android user majorities
Different operating systems means Android and Apple devices have different systems for recipients filtering SMS.
IOS
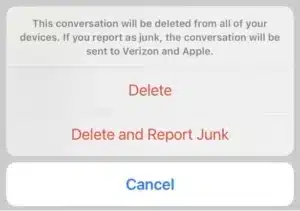
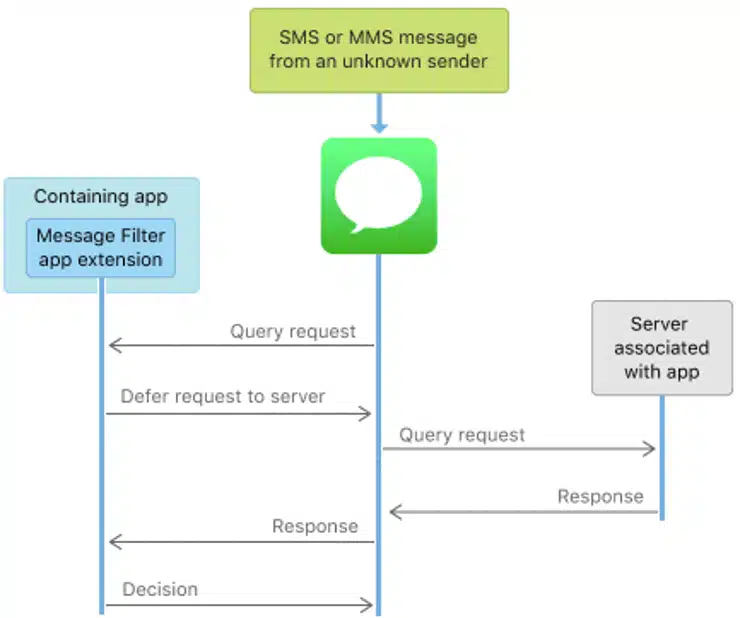
On IOS devices, the user can only read and send SMS through the Messages app, and must install an app extension if they wish to filter messages they receive from unknown senders. There are two extensions available; the message filter app, which decides which folder the user’s messages go into, and an app for reporting unwanted communications to the network.
Spam reporting on IOS
Although Apple may use a third-party server to filter messages, both the filter request and the response go through the Apple controlled Messages interface. The message goes into the appropriate folder without the third party being able to access the messages.
Message filtering through the Apple Messages app
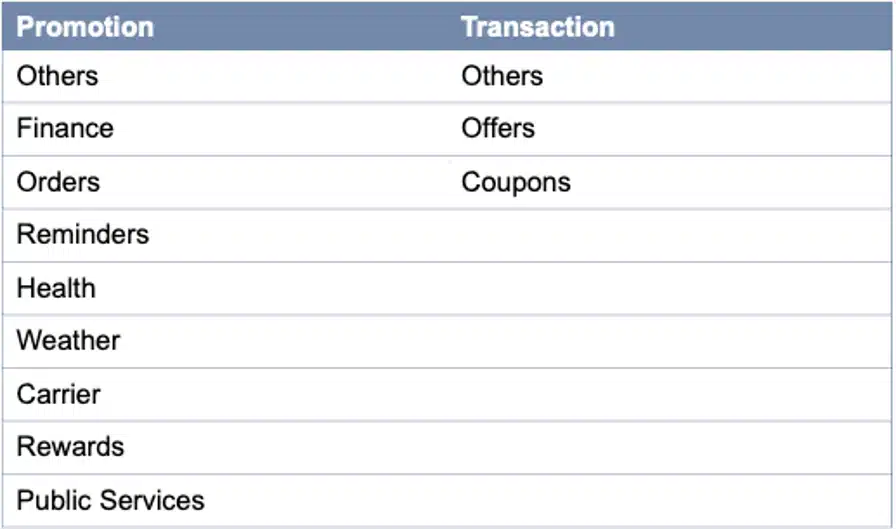
Message filtering categories available on IOS device
Android
Since Android defaults to the Google messaging app, messages are automatically categorized by Google and the process does not involve any interfaces from other developers. Messages are filtered into four categories:
- Personal
- Transactions
- Offers
- One Time Passwords (These are deleted after 24 hours)
Android also offers users a shortcut to report spam messages to 7726 (spam reporting service). The new Google messages App will actually report spam to Google messages and your carrier. It’s also worth noting that while Apple does not permit users to install third party Apps to read messages, Android does.
What are the Implications for Sending Brands?
Now that we have covered how SMS filtering works, let’s discuss the implications for business messaging. There are three primary concerns for sending brands:
1. Read Rates:
If a brand sends a message, and that message goes into a folder that the user doesn’t access often, then the message is less likely to be read.
2. Trustworthiness
Filtering could have an impact on how much the recipient trusts your message, especially if it is filtered into a user’s junk folder.
3. Spam Reporting
Interface often controls behaviour. When it becomes easy to report a message as spam, especially with users having different definitions of what counts as spam, then reporting will happen more often. Enea AdaptiveMobile Security’s threat intelligence team have seen this reflected in data from spam reports coming from IOS devices.
What does the ecosystem need?
What stakeholders in the messaging ecosystem are impacted by message filtering, and how can their needs be addressed?
Developers who provide message filtering Apps need trusted data and intelligence, in order to make decisions on how messages should be filtered.
Senders need to know where their messages will end up – they want to prevent them from entering spam or junk folders.
Networks need more guidance on how they should handle these spam reports. At the moment it is a balancing act; operators don’t want to let bad traffic through, but they can’t simply block it without good traffic being blocked too. This is where trusted messaging intelligence comes in, enabling operators to make informed decisions on what traffic should and should not be let through.
The message filtering tools available today, and what they will become in the future, will continue to impact business messaging. Stakeholders in the industry will need adapt, and learn how to work with this functionality rather than against it, optimizing messaging services while ensuring the security of subscribers.
Enea AdaptiveMobile Security’s mobile network protection is present in over 80 operators, providing state-of-the-art protection through the correlation and analysis of more than 48 billion dark data events every day. Some of our threat intelligence insights, including spam visualisations, are available on our website right now. If you want to find out how our award winning SMS firewall and threat intelligence protects mobile networks, CPaaS, and subscribers against SMS spam and phishing threats, read more here, or reach out to us directly.